
Quick Links
10 Technical SEO Optimization Tips For Increased SEO Rankings
Technical SEO factors represent site design elements that impact website indexability, security, architecture, speed, and mobile-friendliness. To increase search engine ranking and sales leads, follow these 10 SEO optimization tips.
1. Use HTTPS to secure website.
2. Utilize robots.txt correctly.
5. Improve site page load speeds.
10. Fix Client-side 40x errors.
#1) Use HTTPS To Secure Website.
 Google has confirmed that a secure website with an SSL certificate will have an advantage over other websites that are not as secure and encrypted – provided other search engine optimization (SEO) factors remain the same.
Google has confirmed that a secure website with an SSL certificate will have an advantage over other websites that are not as secure and encrypted – provided other search engine optimization (SEO) factors remain the same.
HTTPS Best Practices:
✔️ HTTPS is a must for any website.
✔️ Redirect your users and search engines to the HTTPS page or resource with server-side 301 HTTP redirects.
✔️ Make sure your certificate is always up to date and working correctly.
✔️ Check you have obtained a certificate for all hostnames that your site serves.
✔️ For example, if your certificate only covers www.example.com, a visitor who loads your site using just example.com (without the “www.” prefix) will be blocked by a certificate name mismatch error.
✔️ Make sure your web server supports Server Name Indication (SNI) and that your audience uses supported browsers.
✔️ Embed only HTTPS content on HTTPS pages.
#2) Utilize Robots.txt Correctly.
Robots.txt is a text file residing in the root directory of your website that tells search engines as to which pages of your site they can crawl and add to their index.
Not all pages are equally important in SEO value. This is where you can make use of the robots.txt to restrict access to certain parts of your website that are not important for SEO or rankings.
Robots.txt Best Practices:
✔️ Usually, search engines will not index items you have called out in this file. However, if you have content you do not want to be included in their index, the best way is to password protect the particular directory or page.
✔️ A robots.txt file must be placed in a website’s top-level directory.
✔️ Some user agents (robots) may ignore your robots.txt file.
✔️ Each subdomain on a root domain uses separate robots.txt files.
✔️ This means that both blog.example.com and example.com should have their own robots.txt files (at blog.example.com/robots.txt and example.com/robots.txt).
#3) Optimize XML Sitemaps.
An XML sitemap is a file that helps search engines better crawl and understand your website. Its primary purpose is to inform search engines about pages on your sites available for crawling.
XML Sitemap Best Practices:
✔️ Try to direct bots to the most important pages on your site.
✔️ Include only canonical versions of URLs in your sitemap.
✔️ When you don’t want a page to be indexed, you usually want to use the meta robots “noindex,follow” tag.
✔️ Create dynamic XML sitemaps for large sites.
✔️ Create multiple sitemaps if the site includes >50,000 URLs.
✔️ Use consistent, fully-qualified (use https:// or https://www) URLs. (Google will crawl your URLs exactly as listed.)
✔️ Don’t include session IDs from URLs in your sitemap to reduce duplicate crawling of those URLs.
✔️ If you have alternate pages for different languages or regions, you can use hreflang in either a sitemap or Html tags to indicate the alternate URLs.
✔️ Submit XML sitemap to Google using the Search Console Sitemaps tool.
✔️ Alternatively, you can include your sitemap in the Robots.txt file, specifying the path to your sitemap: Sitemap: http://example.com/sitemap.xml.
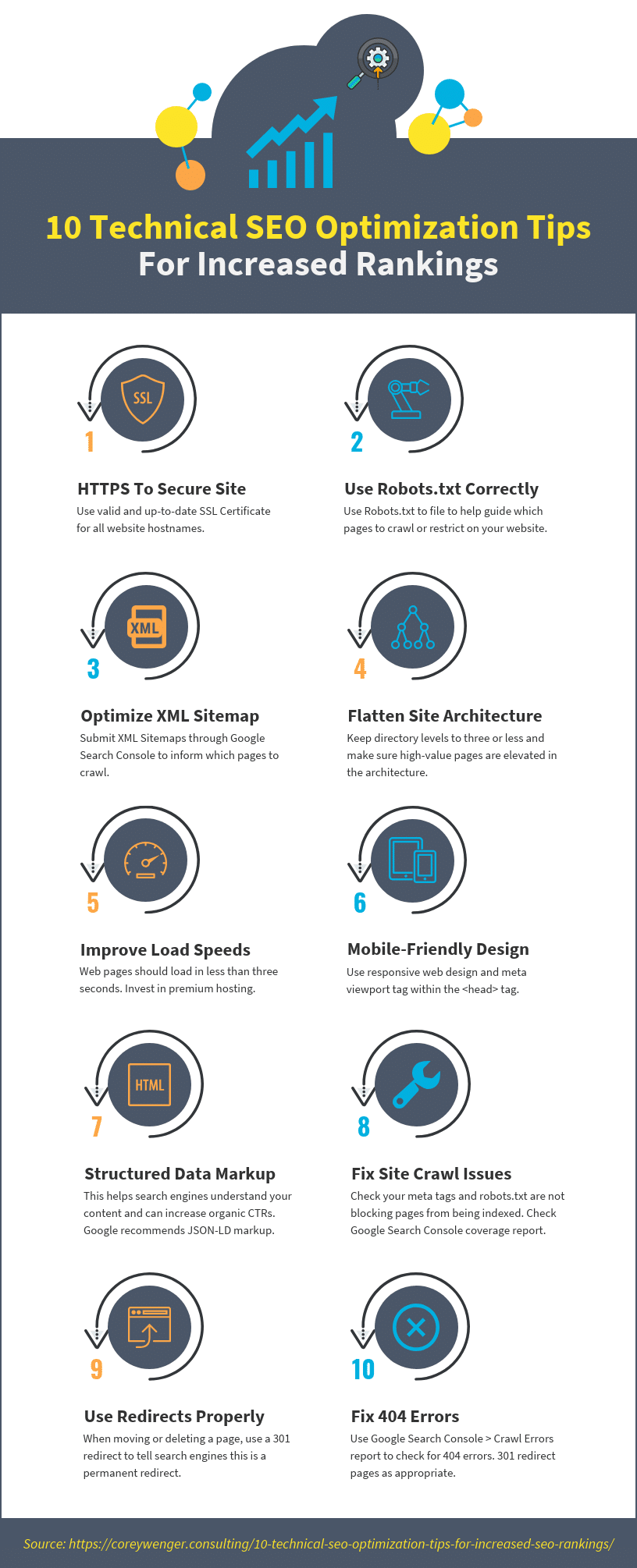
#4) Flatten Site Architecture.
 Site architecture is a way to group and organize content on your site that encompasses URLs, directories, file names, and navigation.
Site architecture is a way to group and organize content on your site that encompasses URLs, directories, file names, and navigation.
Site click depth refers to the number of ‘clicks’ your pages are away from the starting URL. This means target pages should be easily accessible from top-level navigation, footer, or located within a few clicks of these pages.
Generally, the higher the number of clicks (to get to information within the website), the less importance is given to those pages by the search engines.
Site Architecture Best Practices:
✔️ Utilize a flat site architecture, where most pages are within three clicks and where your high-value category pages are elevated in the architecture. (Flat architectures preserve your crawl budgets.)
✔️ Utilize breadcrumb trails to support secondary navigational elements. They help visitors determine where they are on your site.
✔️ Generally, keep your top-level navigation categories to seven or less.
✔️ Create a URL structure that follows your navigation hierarchy.
✔️ Limit the JavaScript in navigation menus.
#5) Improve Site Page Load Speeds.
 Page speeds are measured on a page-by-page basis and mainly impact site conversion rates. Faster page load times help prevent site abandonment (higher bounce rates) and increase visitor engagement (time on site, pages viewed per visitor, and bounce rates).
Page speeds are measured on a page-by-page basis and mainly impact site conversion rates. Faster page load times help prevent site abandonment (higher bounce rates) and increase visitor engagement (time on site, pages viewed per visitor, and bounce rates).
Small increases in total page load times cause site abandonment and lost conversions.
According to a Google study, a one to three seconds delay in page load time can increase site bounce rate by 32%. (Source: Google Mobile Page Speeds.)
Site Page Load Speed Best Practices:
✔️ Web pages should load in less than three seconds.
✔️ Invest in a premium web hosting provider. Aim for a server response time of <200ms.
✔️ Enable compression to reduce file size.
✔️ Implement a caching policy.
✔️ Minify resources – minify HTML, CSS, JavaScript, minify images, videos, and other content if they are slowing down your page speed.
✔️ Optimize CSS delivery.
✔️ Limit the number of resources & requests.
✔️ Use inline small CSS files directly into the HTML to remove small external resources.
✔️ Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
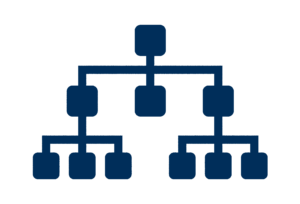
#6) Mobile-Friendly Design.
 According to Google, there are 27.8 billion more queries performed on mobile than desktop. As of September 2020, mobile-first indexing will be the primary index used by Google.
According to Google, there are 27.8 billion more queries performed on mobile than desktop. As of September 2020, mobile-first indexing will be the primary index used by Google.
This means Google crawls every website’s mobile web pages to establish its search engine rankings before it crawls desktop web pages.
Mobile-Friendly Design Best Practices:
✔️ Google will typically notify you when your site has moved to mobile-first indexing within Google Search Console.
✔️ Google will also label your site as last crawled by the Googlebot “smartphone user-agent” in the URL inspection tool as another signal that your site has moved over.
✔️ Responsive web design serves the identical HTML code on the same URL regardless of the users’ device (desktop, tablet, or mobile), but can render the display differently based on the screen size. Responsive design is Google’s recommended website design preference.
✔️ According to Google, pages optimized for a variety of devices should contain a “meta viewport tag” in the head of the document.
✔️ A meta viewport tag provides browser instructions on how to control the page’s dimensions and scaling. Use a meta name=”viewport” tag to tell the browser how to adjust the content. (Source: Google.)
<meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1″>
Incorporate width=device-width to match the screen’s width in device-independent pixels.
Include initial-scale=1 to establish a 1:1 relationship between CSS pixels and device-independent pixels.
✔️ Confirm your page is accessible by not disabling user scaling.
✔️ Be sure not to block the crawling of any page assets (CSS, JavaScript, and images) for any Googlebot using robots.txt or other methods. Fully accessing these external files will help our algorithms detect your site’s responsive web design configuration and treat it appropriately.
✔️ JavaScript-adaptive: In this configuration, all devices are served the same HTML, CSS, and JavaScript content.
✔️ When the JavaScript is executed on the device, the rendering or behavior of the site is changed. If a website requires JavaScript, this is Google’s recommended configuration.
#7) Structured Data Markup.
 Structured data is code you can add to your web pages visible to search engine crawlers. This helps crawlers understand the context of your site content. (It is a way to describe your data to search engines in a language they can understand.)
Structured data is code you can add to your web pages visible to search engine crawlers. This helps crawlers understand the context of your site content. (It is a way to describe your data to search engines in a language they can understand.)
Structured Data can help you enhance the presentation of your listings (and increase organic click through rates) in the search engine result pages (SERPs) either through featured snippets or knowledge graph entries.
Structured Data Markup Best Practices:
✔️ Use schema markup on only pages where it makes sense.
✔️ Microdata and JSON-LD are two ways to mark up your data using the schema.org vocabulary. It’s best to choose either microdata or JSON-LD and avoid using both types on a single page or email.
✔️ Google prefers the use of JSON-LD.
✔️ The JSON-LD version is usually added to the <head> of the page.
✔️ Open Graph is a type of markup used by Facebook to parse out information like what image and description to display. (Please note – it doesn’t replace schema markup.)
✔️ Use markup for a specific product, not a category or list of products.
✔️ You can use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper to markup your pages.
#8) Fix Website Indexability Issues.
Crawl errors mean that Google is having trouble viewing the content on your site.
Typically, Google Search Console is used to determine site indexability/crawl errors. This tells you how many of your websites’ pages are indexed by Google.
Things that impact your crawl:
✔️ Broken or lost internal links.
✔️ If your site is built primarily with JavaScript, especially if your links are in JavaScript, crawlers can have problems parsing links.
✔️Meta Tags or robots.txt telling bots not to crawl certain areas of the site.
✔️ Lots of 5xx or 4xx errors in your crawl results.
✔️ If your server error rate increases, Googlebot will throttle back its requests to avoid overloading your server.
Website Indexability Best Practices:
✔️ Use Google Search Console > Coverage report to examine your crawl history. Use this report to learn which of your pages have been indexed, and how to fix pages that could not be indexed.
✔️ To improve search engine rankings, your most important content should be in HTML text format.
✔️ Images, Flash files, Java applets, and other non-text content are often ignored or devalued by search engine crawlers, despite advances in crawling technology.
✔️ No orphan pages. All website pages need to be part of the overall site architecture.
✔️ Utilize a good internal linking strategy (interlink pages in natural, related topics) and breadcrumbs.
✔️ Reduce the excessive page load time for dynamic page requests. Dynamic pages that take too much time to load can result in time-out issues.
#9) Use Redirects Properly.
A redirect is a way to send both users and search engines to a different URL from the one they originally requested.
The most used redirects are 301, 302, and 307 redirects. 301 redirects are permanent, and 302/307 redirects are temporary.
Please note: Meta Refreshes are a type of redirect executed on the page level rather than the server level. They are usually slower, and not a recommended SEO technique.
Redirect Best Practices:
✔️ Always use 301 redirects when permanently redirecting a page.
✔️ If using 302 redirects incorrectly for permanent redirects, change these to 301 redirects.
✔️ Before you delete a page, setup 301 redirects (and test the redirect is working properly.)
✔️ Use a canonical URL when it is more appropriate.
✔️ Identify site errors by using Google Search Console.
✔️ When using 301 redirects, redirect the user/search engine to the most relevant live page.
✔️ If rebranding a site (using the new domain), use 301 redirect pages from your old site to your new site.
✔️ To implement a 301 redirect for websites hosted on servers running Apache, utilize the .htaccess file.
✔️ Audit your redirected URLs at least once per month.
#10) Fix Client-Side 40x Errors.
 There are several client-side errors that can occur (401 and 403), but the most common is a 404 error, which generally happens when traffic is directed to a page that no longer exists.
There are several client-side errors that can occur (401 and 403), but the most common is a 404 error, which generally happens when traffic is directed to a page that no longer exists.
40x Error Best Practices:
✔️ Utilize custom 404 error pages to keep traffic on your website.
✔️ 404 pages with inbound links or significant inbound traffic should be 301 (permanently redirected) to a similar piece of content on your site.
✔️ Log into your Google Search Console (GSC). Navigate to crawl> Crawl Errors. You will see a list of 40x errors on your site.
✔️ As a simple rule, anytime you have web pages that have decent website traffic and inbound links pointing to them, set up a 301 redirect to manage them.
Final Thoughts
It this article, we discussed ten technical SEO factors that can impact SEO rankings, which range from flattening site architectures to fixing 404-page errors. By addressing these SEO factors, you can increase SEO rankings, boost sales leads, and drive sales growth.
SEO audits are a great way to quickly find and address technical SEO issues that could harmfully affect your search engine rankings. Follow this link to learn more about Corey Wenger SEO Audits.
Learn more about Corey Wenger National SEO Consulting Services, Local SEO Consulting Services, SEO Consultant Services, Technical SEO Audits or SEO Audit Services.
About the Author
Corey has over 20 years of Digital Marketing and SEO experience and is the owner of Corey Wenger SEO Consulting. Corey is an SEO Expert and Consultant and has deep knowledge in troubleshooting, educating, coaching, guiding, and scaling your SEO Strategies and tactics so that you can increase keyword rankings, leads, and sales. Additionally, Corey helps businesses develop SEO Strategies to compete more effectively against search engine competition. Corey is also an SEO Trainer and enjoys helping his clients learn and master SEO tactics, tools, and strategies.
Ready to get your SEO Audit started?

